 Lung
-- organ in which bronchi become highly branched and in which
respiratory exchange occurs. Lung
-- organ in which bronchi become highly branched and in which
respiratory exchange occurs.
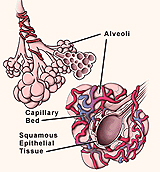
Study the functional organization of lung tissue as shown, noting
especially the extra- and intrapulmonary airways and the
intrapulmonary blood circulation around the alveoli.
Examine an H&E-stained section of the
lung.
Indicate the function of the
cells that air contacts as it moves deeper and deeper into the lung?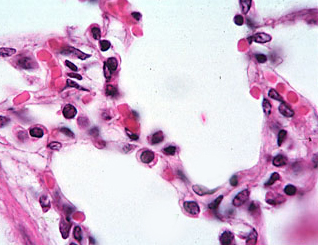
What is the major histological difference between the conducting and
the respiratory portions of the airway?
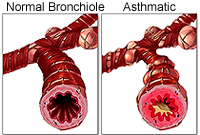 Clinical note: Asthma involves
hyperirritability of the respiratory passages, expressed as
contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle, edema of the mucosa, and
increased mucus secretion. It may be transient, following an upper
respiratory tract infection, but more commonly the sensitization has
an immunological basis and the symptoms are episodic. Re-exposure to
an airborne antigen such as pollen causes release of histamine from
mast cells and eosinophils, precipitating immediate
bronchioconstriction and labored breathing. Various drugs are
helpful in minimizing the severity of the attacks. Clinical note: Asthma involves
hyperirritability of the respiratory passages, expressed as
contraction of the bronchial smooth muscle, edema of the mucosa, and
increased mucus secretion. It may be transient, following an upper
respiratory tract infection, but more commonly the sensitization has
an immunological basis and the symptoms are episodic. Re-exposure to
an airborne antigen such as pollen causes release of histamine from
mast cells and eosinophils, precipitating immediate
bronchioconstriction and labored breathing. Various drugs are
helpful in minimizing the severity of the attacks.
Pneumocytes and
macrophages. |