|
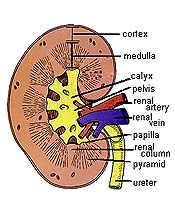 Kidney
-- a bean-shaped organ with renal arteries and veins entering with
the ureter at the hilum. Kidney
-- a bean-shaped organ with renal arteries and veins entering with
the ureter at the hilum. After
studying
the diagrams showing the overall organization of the kidney and the
note the arrangement of the components in nephrons, see if
you can identify its basic components.
Examine a section of stained section of the kidney
- Note the thin fibrous capsule
and the fibrous/fatty support tissue at the hilum area
surrounding the renal pelvis. The orientation of
this section does not clearly show the kidney's internal
organization. .
- With low power, identify the
cortex and the medulla.
- Near the corticomedullary
junction can be several sets of arcuate arteries and veins cut transversely. (The veins still contain blood.) Still
with low power, identify in the cortex renal corpuscles and then the medullary rays converging on the renal
papilla and calyx.
- Note that the largest collecting
ducts (the ducts of Bellini) converge to form the renal papilla,
and that this is surrounded by the calyx composed of
transitional or urinary epithelium.
Name a simple squamous
structure in the cortex.
How does the structure of the proximal convoluted tubule cells
relate to their
function?
Compare and contrast the cells of the proximal convoluted tubule
and the distal convoluted tubule.
What is the general function of the loop of Henle?
Kidney stones
and the renal cortex. |