|
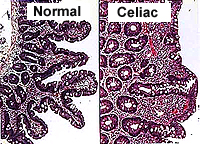 Clinical note: A
disorder called celiac disease, celiac sprue, or gluten-induced
enteropathy, is characterized by intolerance to gluten (a protein in
many grains) and results in disappearance of enterocyte microvilli
and flattening of the villi and subsequent malabsorption of
nutrients. Regeneration of these structures in the small bowel and
return of normal nutrient absorption occur after a few weeks on a
diet lacking gluten. Clinical note: A
disorder called celiac disease, celiac sprue, or gluten-induced
enteropathy, is characterized by intolerance to gluten (a protein in
many grains) and results in disappearance of enterocyte microvilli
and flattening of the villi and subsequent malabsorption of
nutrients. Regeneration of these structures in the small bowel and
return of normal nutrient absorption occur after a few weeks on a
diet lacking gluten.
What is the function of the
Paneth cells?
What is the function of the muscularis mucosae in the ileum?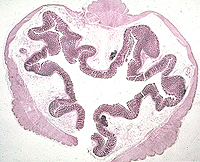
Large Intestine -- site for
absorption of water and elimination of solid waste. The three
regions (cecum, colon, and rectum) are not very different
histologically. Examine a section of the colon and identify the major layers and sublayers.
- Note that the outer layer of
muscularis (cut transversely here) does not completely surround
the inner layer, but is separated into three more-or-less
distinct muscles, the taeniae coli.
- Also, note that myenteric plexi
are distinct on this slide.
- The mucosa and submucosa are
highly folded in this specimen.
- The mucosa is invaginated into
many straight, tightly packed colonic glands, lined by
columnar mucus-secreting cells.
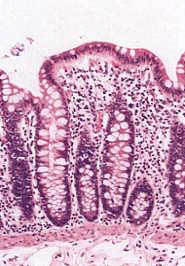
- In the lumen, note the solid
waste and indigestible material covered with mucus.
Indicate three histological
features of the colon which clearly pertain to its function.
Now for the
digestive glands and liver.. |