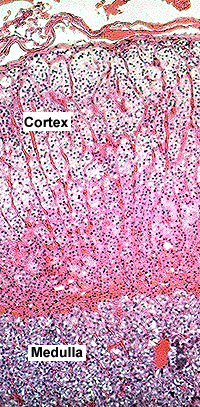
 Adrenal gland -- consists of
two endocrine tissues (cortex and medulla) that are functionally distinct.
These are flattened glands with concentric layers of secretory tissue. In the distinct capsule associated
with adipose tissue, notice the small arteries entering the gland
and the vascular plexus just inside the capsule.
Examine the cortex and identify the three layers or zones in which
the steroid-secreting cells have slightly different arrangements,
with groups of cells separated by fine, well-vascularized support
tissue septa.
- The outermost zona glomerulosa has cells
secreting mineralocorticoids arranged in irregular rounded clumps ("glomeruli").
- The middle and widest layer, the
zona fasciculata, has
cells making glucocorticoids arranged in strands ("fascicles").
- The
innermost layer, the zona reticularis, shows irregular,
branching ("reticular") cords of cells secreting small quantities of
sex hormones (androgens).
- Salt, sugar, sex is the organization.
Compare and contrast the 3
zones of the adrenal cortex.
What is the embryological origin of the adrenal medulla?
Thyroid is next. |