| Connective tissue supports other
tissues and connects all of the body’s tissues and organs together.
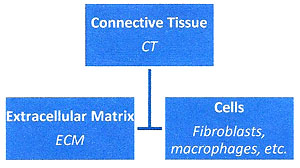
In contrast to epithelium which is composed mainly of cells,
connective tissues (CT) consist of material between or outside of
cells, largely fibers and a gel-like ground substance. Cells tend to
be widely separated among the masses of fibers and ground
substances. The fibers and the
ground substance are collective termed the extracellular matrix (ECM).
The fibers, composed primarily of collagen or elastin, are
responsible for the tensile strength and elasticity of the tissue.
The ground substance, substantially composed of hydrated
proteoglycans, provides the medium through which dissolved
substances pass from capillaries to cells and back.
Connective tissue is organized
with cells and material outside of cells.
Objectives:
- Identify and recognize the LM
and TEM characteristics of extracellular matrix components,
including both ground substances and fibers, and understand
their functional significance.
- Recognize the LM appearance and
function of the major cell types normally found in the different
types of connective tissue
- Recognize the traditional types
of connective/support tissue and their functional significance
Extracellular
matrix |