Mucosa-associated Lymphoid Tissue
(MALT)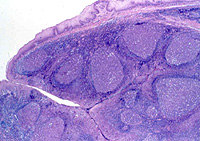
Examine a section of tonsil. Identify the stratified squamous epithelium covering
the tonsil and the dense connective tissue at its base. Identify the
large lymphoid follicles. The large, pale cells scattered among the
lymphocytes in the follicles are macrophages acting as
antigen-presenting cells.
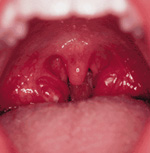 Clinical
note: Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and other upper respiratory
tract infections are among the most common problems involving the
head and neck. Tonsillectomies, which were formerly much more common
than now, may be required if chronic tonsillitis causes enlargement
of the affected structures to the degree that air passages are
obstructed. To the right we see a pair of very large and inflamed
tonsils. Clinical
note: Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and other upper respiratory
tract infections are among the most common problems involving the
head and neck. Tonsillectomies, which were formerly much more common
than now, may be required if chronic tonsillitis causes enlargement
of the affected structures to the degree that air passages are
obstructed. To the right we see a pair of very large and inflamed
tonsils.
Examine the connective tissue in the
wall of the ileum and identify the nodule of
lymphoid tissue representing a Peyer's patch. Similar
diffuse nodules of various sizes will be seen in sections of
esophagus and many regions of the small and large intestines.
In what sense is the MALT
system the first line of the body’s defense?
Does it resemble more closely a
lymph node or a thymus?
The spleen is
next. |