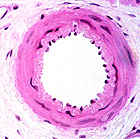
 The
smallest branches of arteries are called arterioles (Fig.
11-11), a term often used when the tunica media has only 2-3
layers of smooth muscle. (Arterioles with only 1 or 2 layers
of smooth muscle fibers are sometimes called "metarterioles".) The
smallest branches of arteries are called arterioles (Fig.
11-11), a term often used when the tunica media has only 2-3
layers of smooth muscle. (Arterioles with only 1 or 2 layers
of smooth muscle fibers are sometimes called "metarterioles".)
Compare and contrast the muscular artery and the elastic
artery.
What is major difference between these arteries and an elastic
artery, besides their size?
How does the muscle in the large vessels differ from that in the
heart?
Capillaries usually have
narrow lumens, often no more than the diameter of
erythrocytes.
Sinusoids have much larger lumens,
but are present in only certain organs, such as bone marrow, where
you examined them previously.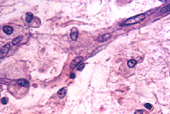
- Both capillaries and sinusoids
lack muscular and adventitial layers. Fig. 11-16 compares the
three major types of capillaries.
- Examine capillaries (Fig. 11-15) in
skeletal muscle (slide 8) and in the CT of mesentery (slide
116). Look carefully for pericytes.
Examine the electron micrographs of
the two common types of capillaries (Figs. 11-17 and 11-18),
noting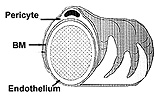 particularly the pinocytotic vesicles often present and the
fenestrations in one type. particularly the pinocytotic vesicles often present and the
fenestrations in one type.
What is the functional
significance of the differences in capillary endothelium?
The lymphatic
vessels are next.
|