|
Introduction
Case1:
Vomiting
Case 2:
Cough & fever
Case 3: Bruising
Case 4: Sore
throat
Case 5: Jaundice
Case 6: Flu & fever
Case 7: Diarrhea
Case 8: Black
Robe
Case 9: Back Pain Catching the
beast
Thanks to
Quiz
Please |
|
Rounding up the
usual suspects.
- Although culture is most obvious,
it's not the only way of identifying the offending agent, or monitor the
progression of an infectious disease.
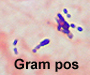
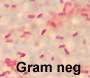
- Gram stain. This is pretty obvious,
but often overlooked.
- Be suspicious of the specimen if no PMNs
are present. If it's acutely inflamed there should be.
|
 |
- If you are going to culture, be
sure
- It's collected properly and
- Transported to the lab promptly.
- For aerobic bugs you should get
- An identification of potential
pathogens,
- And an antibiotic sensitivity
pattern.
|
 |
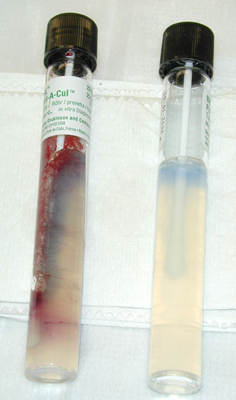
- Anaerobes are different case altogether.
- They require a special transport medium.
- Be careful of the swab, Rayon or
Dacron are best
- Natural fiber (cotton & wood)
contain fatty acids that may inhibit some bugs.
- You may have to actually send tissue.
- Don't expect an antibiotic sensitivity
panel.
|
 |
Other ways of identifying the bug.
Back |