 The
main function of the respiratory system is the transferring of gases
between the air and the blood. The
main function of the respiratory system is the transferring of gases
between the air and the blood.
The system is comprised of tubes and highly branched channels which
terminate in dead-end sacs where gas transfer occurs. Air brought
into the body is first conditioned and filtered in the first part of
the respiratory system, the conducting portion (nasal cavity to
bronchioles). The second part of the system, the respiratory
portion, consists of the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli are
involved with gas exchange.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the structure and
functions of the conducting portion of the respiratory system.
- Recognize and describe
respiratory epithelium and the functional significance of its
structural features.
- Understand the structures of the
larynx, trachea, and bronchial trees.
- Understand the structure and
functions of respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and
alveoli.
- Recognize and understand the
functions of type I and type II pneumocytes and alveolar
macrophages.
- Recognize and understand the
layers in the barrier between blood in alveolar capillaries and
air in the alveoli.
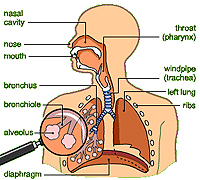
- The basic anatomy of the upper
respiratory tract is shown in the diagram on the next page.
Let's start at the top with
the nasal cavity. |