Learning Objectives for
connective tissue:
- Be able to identify the major
types of connective tissue and understand how the structure of
each reflects its function.
- Understand how to distinguish
the various cells found in connective tissue (fibroblasts,
adipocytes, mast cells, plasma cells, macrophages, and
undifferentiated mesenchymal cells) and to describe their
functions and key features
- Know the composition,
morphology, and variations in distribution of the ground
substance and the three types of extracellular fibers and their
functions.
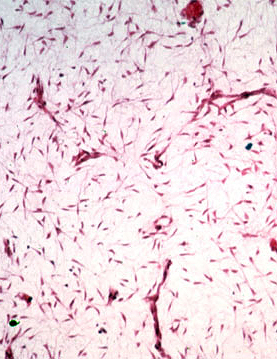
We will start with primitive
(embryonic) connective tissue: mesenchyme (Fig 5-1).
- Examine the cross section of a
mammalian embryo (slide 91) and locate regions of mesenchyme
within and around the developing organs.
What are some major differences
between mesenchymal cells and epithelial cells?
What is the fibrous material
between the mesenchymal cells and what does the "empty" space around
the fibers represent?
Let's now take a look at the
common forms of mature connective tissue. |