Examine
the lens. Identify the capsule and cuboidal epithelium,
nucleated fibers, and older non-nucleated fibers (Fig. 23-12).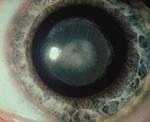
How does the lens focus light onto the retina?Clinical note:
Oxidative changes in the lens fibers are common as one ages and can
lead to opacity of lens tissue
called a cataract, which eventually produces
blurred vision. In surgery for cataracts, such lenses are broken up
and aspirated out through a slit in the upper cornea, leaving the zonule
and thick posterior capsule of the lens in place to hold an
implanted plastic lens. The two images to the right show what a
cataract lens looks like and what a person sees with such a lens.
Examine the iris, noting the
continuity with the ciliary body.
- Identify the heavily pigmented
surface epithelial layers, the stroma, the constrictor muscle at
the pupil, and the dilator muscle of the pupil (Fig. 23-11).
Identify the anterior and posterior chambers meeting at the
pupil.
What cells of the iris determine
the color of one's eyes?
What substance moves through the
pupil?
Why are the two muscular
structures in the iris difficult to study histologically?
Now for the
cornea. |