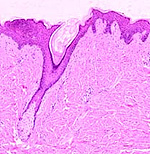
 Thin
skin -- present on most of the body and similar in many respects
to thick skin, but much thinner overall, with hair follicles and
without the features for detecting and protecting against
pressure/friction. Thin
skin -- present on most of the body and similar in many respects
to thick skin, but much thinner overall, with hair follicles and
without the features for detecting and protecting against
pressure/friction.Examine
slides 36 and
157,
- Note the differences in thin skin
with regard to the dermis and the epidermal strata (Fig. 18-3).
- Identify melanocytes (Fig.
18-6), which are also seen on
slide 5.
 What is the mechanism by which
keratinocytes become pigmented? What is the mechanism by which
keratinocytes become pigmented?
Clinical note: Vitiligo is an
acquired patchy loss of pigment in the skin, due to a localized
autoimmune reaction to the melanocytes.
Now for skin
appendages. |