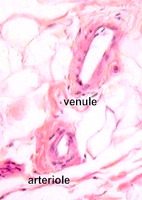
 Venules
collect blood from capillary networks and gradually merge to form
veins. Venules
collect blood from capillary networks and gradually merge to form
veins.Examine the examples of
venules (Fig. 11-20) and small veins (Fig. 11-21) in CT (slides
45,
8,
116).
- Compare the size, wall
thickness, and other structural features of venules and
arterioles.
What differences are evident
between arterioles and venules?
Why are vessels of the
microvasculature frequently difficult to classify histologically?
 Examine
examples of medium size veins (Fig. 11-21c,d) in
slide 92 and identify the 3 layers or tunics seen earlier in
arteries. Examine the structure of valves in veins (Figs.
11-21 and 11-22). Examine
examples of medium size veins (Fig. 11-21c,d) in
slide 92 and identify the 3 layers or tunics seen earlier in
arteries. Examine the structure of valves in veins (Figs.
11-21 and 11-22).
What is the function of the
valves?
Clinical note: Weakness in the
walls or valves of veins can lead to abnormally dilated or varicose
veins, which most commonly occur in the lower legs where backflow of
blood is particularly common due to the pull of gravity.
Examine a section of a large vein
(slide 16; Fig. 11-22) and note how the thickness of the wall and its
various layers compare to the wall of the neighboring artery.
The lymphatic
vessels are next. |