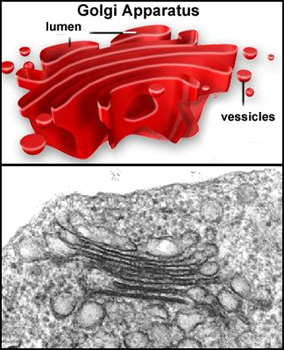
 Golgi
apparatus is a group of flattened membranous cisternae formed from
vesicles that pinch off of the ER and coalesce. Golgi
apparatus is a group of flattened membranous cisternae formed from
vesicles that pinch off of the ER and coalesce.
- Polypeptides in the cisternae
are glycosylated and otherwise modified in the Golgi complex.
- At the “maturing” face of the
Golgi, new vesicles pinch off and are sorted to different
destinations according to their contents.
- Most such vesicles either
secrete their contents by exocytosis or remain in the cytoplasm
as lysosomes or peroxisomes.
- The Golgi is generally difficult
to see by LM, but examine the ultrastructural views and diagrams
of this structure in Figures 2-20 through 2-23.
Describe the movement of
proteins from synthesis in the rER through secretory granules about
to undergo exocytosis.
Give some reasons why Golgi
complexes are usually hard to see with the light microscope.
Lysosomes are
next. |