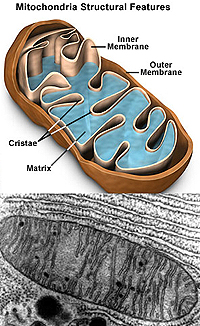
 Mitochondria
consist of an outer membrane and a highly folded inner membrane and
are generally tubular in shape. Mitochondria
consist of an outer membrane and a highly folded inner membrane and
are generally tubular in shape.
- Mitochondria are usually not
seen with the LM unless special stains or histochemical
techniques are used (Fig. 2-11).
- Histochemical staining here uses
specific enzymes of the citric acid cycle, which are only found
in mitochondria, to generate the color seen.
- Examine ultrastructural
views of mitochondria in Figures 2-12 and 2-20b.
Why are mitochondria sometimes
considered to be “semiautonomous”, compared to other organelles?
What is the functional
significance of the mitochondrial cristae? Of the mitochondrial
matrix?
Less fundamentally important than the organelles
mentioned so far, inclusions are cytoplasmic accumulations of various cell
products which are not membrane-bound.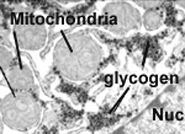
- Examples are lipid droplets,
glycogen granules, and melanin granules (all shown
in Fig. 2-35.)
- Lipid requires special fixation
and staining to be seen, glycogen usually requires a special
stain, but melanin requires no stain.
Why are the three types of
inclusions listed above not found in all cells?
The next unit deals with
stem cells and apoptosis. |