|
Clinical note: The
inflammatory condition known as glomerulonephritis results from an autoimmune cross reaction on the part of the host against
streptococcal antigens. Infections triggering this reaction can
occur in either the skin or throat. The inflammatory
response is largely confined to the glomeruli, damaging the
capillaries and basal laminae to the extent that proteins and
erythrocytes may appear in the urine. The injury results from
antigen-antibody complexes getting stuck in the glomerular filter.
 After
studying the figures and slides of the kidney, see i you can name the epithelial type and major function of each of the
following: After
studying the figures and slides of the kidney, see i you can name the epithelial type and major function of each of the
following:
- PCT:
- Loop of Henle, thin limb:
- Loop of Henle, thick limb:
- DCT:
- Collecting tubule:
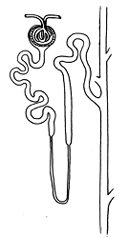
How do the histological
features at different levels of the nephron correlate the major
cellular activities or functions at these regions?
Examine glomeruli and se if you
can
locate one showing the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
- Identify the macula densa in the distal convoluted
tubule.
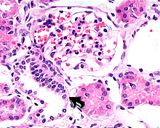
- Try to identify the specialized smooth muscle
juxtaglomerular cells and the lacis cells (Fig. 19-12), although
these will be difficult to find in most glomeruli.
What does the
juxtaglomerular apparatus do and how does it do it?
Now for the
ureter and urinary bladder.
|