 The
oral (or buccal) cavity contains structures for ingestion and
fragmentation of food, resulting in formation of a bolus of food for
swallowing. We have already studied teeth. In this lab note the
abundance of skeletal muscle and small salivary glands in the lip.
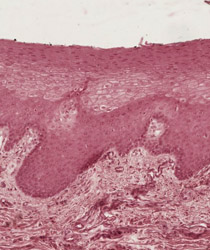
The skin on the external surface merges into the nonkeratinized,
stratified squamous epithelium of the oral mucosa on the internal
surface. The
oral (or buccal) cavity contains structures for ingestion and
fragmentation of food, resulting in formation of a bolus of food for
swallowing. We have already studied teeth. In this lab note the
abundance of skeletal muscle and small salivary glands in the lip.
The skin on the external surface merges into the nonkeratinized,
stratified squamous epithelium of the oral mucosa on the internal
surface.
What are the major differences
between oral mucosa and skin?
Soft Palate
- Oral Mucosa
- Stratified Squamous
(non-keratinized) Epithelium
- Nasal Mucosa
- Pseudostratified Ciliated
Columnar Epithelium
- Mucous Glands
Stratified squamous (non-keratinized)
epithelium lines the oral surface of the soft palate and
interdigitates with the lamina propria. The soft palate contains
mucous glands that secrete their product into the oral cavity.
Why would you expect that the
epithelia lining the soft palate and the nasal cavity are so
different?
Now for the
esophagus. |