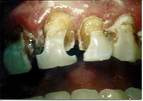
 Clinical note: The oral
cavity has a large and varied bacterial flora. Bacteria may
accumulate and form a layer (plaque) on a tooth, releasing acids
that demineralize the enamel and dentine and produce dental
cavities. Other bacteria proliferating in the gingival cleft may
destroy the periodontal ligament, cause resorption of alveolar bone,
and loosening of teeth. Clinical note: The oral
cavity has a large and varied bacterial flora. Bacteria may
accumulate and form a layer (plaque) on a tooth, releasing acids
that demineralize the enamel and dentine and produce dental
cavities. Other bacteria proliferating in the gingival cleft may
destroy the periodontal ligament, cause resorption of alveolar bone,
and loosening of teeth.Ground
Tooth:
Which hard component of the
tooth most resembles bone histologically?
What do the parallel line (rods or prisms) in enamel represent?
Examine
a section of developing tooth. See if you can Identify
- The dental pulp,
- Odontoblasts,
- Dentine,
- Enamel
- Ameloblasts
Explain the relationship of
ameloblasts and odontoblasts to the formation of enamel and dentine.
Which layer disappears before
eruption of the tooth and which layer persists?
Now for the
nervous system. |