Stomach --
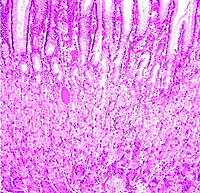 site
where food is converted to a thick fluid for most efficient
enzymatic digestion of macromolecules. site
where food is converted to a thick fluid for most efficient
enzymatic digestion of macromolecules.Examine a section
of the fundic region of the stomach.
- Identify first the layers and
sublayers, noting that the simple columnar
epithelium invaginates into gastric pits, which are tightly
packed together side-by-side
- These lead into the gastric
glands which extend down all the way to the thin muscularis
mucosa. Cells of the lamina propria are seen scattered loosely around the
gastric pits.
What is the function of each
epithelial cell type in the stomach?
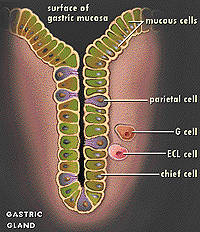 Starting at the surface, identify the mucus-secreting cells (called
surface and neck cells depending on their proximity to the surface
lining the stomach cavity), the large eosinophilic parietal cells,
and the smaller, more basophilic peptic cells. (Image
courtesy of GERD Information Resource
Center) Starting at the surface, identify the mucus-secreting cells (called
surface and neck cells depending on their proximity to the surface
lining the stomach cavity), the large eosinophilic parietal cells,
and the smaller, more basophilic peptic cells. (Image
courtesy of GERD Information Resource
Center)
Why do you suppose most of
these cells are protected down inside the gastric pits/glands?
On to the
pyloric glands and small intestine. |