|
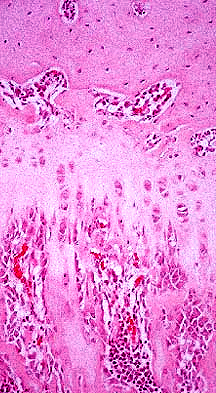 Cartilage
is a form of CT that forms the supportive framework of certain
organs, the articulating surface of bones and the greater part of
the fetal skeleton. The cartilage of the fetal skeleton is
eventually replaced by bone. Three types of cartilage will be
studied in today’s lab: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage and
fibrocartilage. Cartilage is a nonvascular and pliable, yet strong,
material composed of proteoglycan matrix. Embedded in this matrix
are the fibrous and cellular components of cartilage. Cartilage
is a form of CT that forms the supportive framework of certain
organs, the articulating surface of bones and the greater part of
the fetal skeleton. The cartilage of the fetal skeleton is
eventually replaced by bone. Three types of cartilage will be
studied in today’s lab: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage and
fibrocartilage. Cartilage is a nonvascular and pliable, yet strong,
material composed of proteoglycan matrix. Embedded in this matrix
are the fibrous and cellular components of cartilage.
Learning objectives for this unit:
- Recognize the microscopic
features of both the matrix and the cells in cartilage and bone.
- Understand the structural and
functional differences among types of cartilage.
- Understand the microscopic
structure of bone and the functional significance of osteons
Let's take a look at some tissues. |