Cartilage is a specialized,
semi-rigid connective/supporting tissue characterized mainly by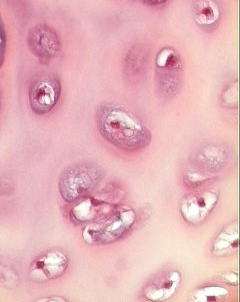
- The predominance of ground
substance in the extracellular matrix.
- The ground substance contains
varying amounts of collagen and elastic fibers, giving rise to
three broad categories or types of cartilage.
Hyaline cartilage, the most
common type, contains the smallest proportion of fibrous material in
its ground substance. Examine the cartilage in the trachea and the
larynx.
- Identify perichondrium,
- Chondroblasts,
- Chondrocytes,
- Lacunae
What is a major physiological
property of hyaline cartilage?
What is the function of
perichondrium?
 Clinical
note: The avascularity of cartilage limits its size
according to the distance small molecules can diffuse through the
matrix to nourish the chondrocytes. The matrix is a barrier to the
entry of large proteins like immunoglobulins and also to
lymphocytes, which is important for the practice of reconstructive
and cosmetic surgery since cartilage can be transplanted from one
individual to another without rejection by the immune system. Clinical
note: The avascularity of cartilage limits its size
according to the distance small molecules can diffuse through the
matrix to nourish the chondrocytes. The matrix is a barrier to the
entry of large proteins like immunoglobulins and also to
lymphocytes, which is important for the practice of reconstructive
and cosmetic surgery since cartilage can be transplanted from one
individual to another without rejection by the immune system.
Fibrocartilage
and elastic cartilage is next. |