Synovial joint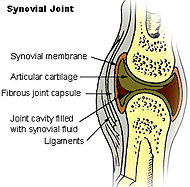
- Note that in this slide the
joint may be too immature to allow specific articular cartilage
to be clearly distinguished as shown in the figures.
- Pay particular attention to the
synovium, or synovial membrane, which is diagnostic for this type of joint.
What type of tissue is the
synovium and what is its function?
What feature(s) of a synovial joint often decrease with age,
requiring the joint to be replaced with a artificial joint?
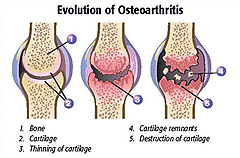 Clinical note: Articular
cartilage normally begins to break down slowly as we age,
potentially leading to inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
This process can be inhibited by regular exercise and full use of
the joints because recurrent pressure on the cartilage and other
parts of joints improves tissue maintenance. Injection of hyaluronan
solution into the synovial cavity is a routine treatment for severe
arthritis. Dietary supplementation with chondroitin sulfate and
glucosamine has also been shown to slow progression of arthritis.
Click the image for a bigger view. Clinical note: Articular
cartilage normally begins to break down slowly as we age,
potentially leading to inflammation associated with osteoarthritis.
This process can be inhibited by regular exercise and full use of
the joints because recurrent pressure on the cartilage and other
parts of joints improves tissue maintenance. Injection of hyaluronan
solution into the synovial cavity is a routine treatment for severe
arthritis. Dietary supplementation with chondroitin sulfate and
glucosamine has also been shown to slow progression of arthritis.
Click the image for a bigger view.
Intervertebral joints
- Understand the relationship
to the fibrocartilage and the periosteum of the vertebral bones.
Teeth are next. |