|
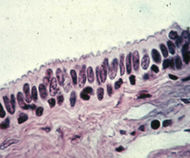 Stratified
cuboidal epithelium. (Fig. 4-14d) Stratified
cuboidal epithelium. (Fig. 4-14d)
- This epithelial type is not
common and is found primarily in the largest ducts of salivary
glands.
- Examine the cross sections of
these on slide 11.
- The epithelium consists of 2 or
3 layers of cuboidal or low columnar cells.
What epithelial type makes
up the smaller ducts seen in slide 11?
Transitional epithelium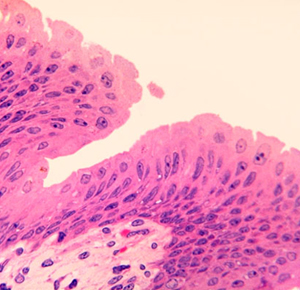 (Fig. 4-15)
(Fig. 4-15)
- This type is found only in
the urinary tract and is highly specialized to resist the toxic
effects of urine and to "stretch".
- Examine the folded lining of
the bladder (slide 12 and
slide 28) and ureter (slide 16).
- The most
distinguishing features are that most of the superficial cells
are
- Rounded, not squamous, and
- The basement membrane is very
thin and is not visible by LM.
- Generally 6 to 8 layers thick.
- The transitional epithelium of the bladder appears to get
thinner and the cells flatten as the organ becomes distended
with urine.
Intercellular
junctions |