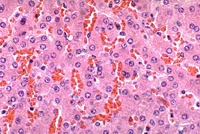
 Examine
the anastomosing plates of hepatocytes between the portal tracts and
the central venule (Figs. 16-11 through 16-14). Examine
the anastomosing plates of hepatocytes between the portal tracts and
the central venule (Figs. 16-11 through 16-14).
- Identify the vascular sinusoids
between the plates of hepatocytes, the endothelial cells lining
the sinusoids, and
- Scattered dark, rounded
macrophages (Kupffer cells) (Fig. 16-14) in the sinusoidal
lining.
Why might the hepatocytes near
the portal tract appear different from those near the central vein?
On slide 24 notice the different
staining properties of hepatocytes in regions of a lobule at various
distances from the portal tract.
- These differences reflect
different metabolic components and other changes in hepatocytes
exposed to blood with different changing levels of oxygen and
metabolites.
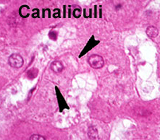 Examine
carefully the ultrastructure of hepatocytes and sinusoids (Fig.
16-15). Examine
carefully the ultrastructure of hepatocytes and sinusoids (Fig.
16-15).
- Identify microvilli projecting
from the hepatocytes into a space beneath the discontinuous
endothelial lining of the sinusoid,
- The perisinusoidal space (of Disse).
- Identify also the channels
present between adjacent hepatocytes,
- The bile canaliculi, into which
bile is secreted, to be drained initially via the bile duct
branch in the portal tract. Bile is both an exocrine and an
excretory product.
What are some substances added
to and removed from blood as it goes through the liver, entering via
the hepatic portal vein, passing through lobules, to its exit via
the hepatic vein?
What is the fate of the
excreted substances removed from blood in the liver?
Now for the
gallbladder. |