 Gall Bladder -- stores and
concentrates bile for release into the duodenum (Fig. 16-20). Gall Bladder -- stores and
concentrates bile for release into the duodenum (Fig. 16-20).
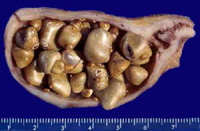
Clinical note: A common disorder of the gallbladder is
cholelithiasis or the formation of gallstones. These are concretions
of cholesterol monohydrate, calcium salts, and phospholipid which
can cause painful inflammation of the gallbladder and/or obstruction
of the cystic duct and distention of the gallbladder. Treatment
often involves surgical removal of the gallbladder.
Examine sections of gall bladder
(slide 94 and
105).
- Identify the major layers and the differences
within the layers found along the GI tract.
- Note the prominent mucosal folds
(Fig. 16-21).
- Also note the type of epithelium
lining the lumen and its very thin basement membrane.
What type of epithelium lines
the gall bladder and what is its function?
How do the folds and the nature
of the epithelial lining facilitate the function of the gall
bladder?
How might “gall stones” begin
to form?
Now for the
endocrine system. |