Cell Biology & Histology A560
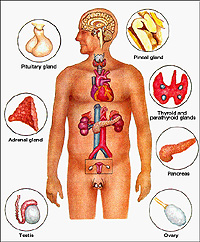 The
organs usually grouped together as the endocrine system represent
many structures with a great deal of morphological and functional
diversity. The fact that they are grouped together reflects
primarily the fact that they all secrete directly into the blood
stream, rather than delivering their products to other sites by
means of ducts, as in exocrine glands. Endocrine glands may be
large, distinct organs, such as those to be studied here, or
scattered groups of cells, such as the pancreatic islets, or
individual cells, such as those found in the mucosa of the digestive
system. A structural feature common to all endocrine tissues is a
very rich vascular supply. Furthermore, in spite of having origins
from diverse kinds of tissues, almost all endocrine glands are
structurally epithelioid in appearance. i.e., they are composed of
sheets, tubes, columns or clusters of closely contiguous cells. A
less universal feature of endocrine cells is a content of granules
suggesting the secretory function of the cells. The
organs usually grouped together as the endocrine system represent
many structures with a great deal of morphological and functional
diversity. The fact that they are grouped together reflects
primarily the fact that they all secrete directly into the blood
stream, rather than delivering their products to other sites by
means of ducts, as in exocrine glands. Endocrine glands may be
large, distinct organs, such as those to be studied here, or
scattered groups of cells, such as the pancreatic islets, or
individual cells, such as those found in the mucosa of the digestive
system. A structural feature common to all endocrine tissues is a
very rich vascular supply. Furthermore, in spite of having origins
from diverse kinds of tissues, almost all endocrine glands are
structurally epithelioid in appearance. i.e., they are composed of
sheets, tubes, columns or clusters of closely contiguous cells. A
less universal feature of endocrine cells is a content of granules
suggesting the secretory function of the cells.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the dual formation of
the embryonic pituitary gland.
- Understand the main divisions of
the pituitary, its relationship to the hypothalamus, and unique
features of its blood supply.
- Know the major cell types of the
adenohypophysis, their hormone products, and the factors
controlling their release.
- Understand the structure of the
neurohypophysis and its functional elements, as well as the source
of its hormone products.
- Identify the main components of
thyroid tissue (follicles, colloid, and stroma) and understand the
mechanism of hormone production and the parafollicular cells of
the thyroid and know their function.
- Identify the main cell types of
parathyroid glands and know their functions.
- Understand the formation and
vascular supply of the adrenal gland and identify the zones of the
adrenal cortex and their hormone secretions, as well as the cells
of the adrenal medulla and know their function.
- Identify pancreatic islet tissue
and know the hormones/functions of the major cell types.
- Recognize the structure of the
pineal gland and know its function.
Pituitary gland |
|