 Pituitary
gland (hypophysis) -- known as the Master Gland because of the
hormonal control it exerts on many other glands Pituitary
gland (hypophysis) -- known as the Master Gland because of the
hormonal control it exerts on many other glands
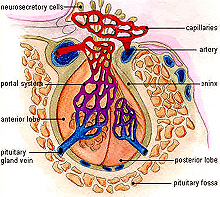
Study the diagram of the pituitary gland
(Fig. 20-2) noting the relationship among the anterior and posterior
parts, the vascular supply, and the hypothalamus of the brain.
What does the pituitary portal
system transport that makes it important functionally?
Examine a section of pituitary (slide
128, 103) and identify the
anterior pituitary, the posterior pituitary,
and the intervening pars intermedia with cysts representing
remnants
of Rathke's pouch (Figs. 20-4 and 20-9). The latter structure may be
better seen on slide 122. The pars intermedia is poorly developed in
humans. Note the
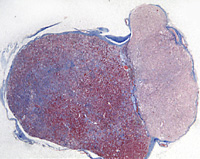 abundance
of large capillaries among the clumped, epithelial cells in the
anterior pituitary. abundance
of large capillaries among the clumped, epithelial cells in the
anterior pituitary.
How do the two major parts of
the pituitary gland form in the embryo?
Slide 74 shows a section of pituitary
gland prepared with a special trichrome stain that demonstrates the
different staining properties of the secretory cells in the anterior
pituitary. Identify acidophils, basophils, and chromophobes (Fig.
20-6).
Indicate 5 hormones secreted by cells
of the anterior pituitary and explain a technique by which the cells
secreting each of the hormones could be located?
Examine the ultrastructural
features of acidophils and basophils in Fig. 20-7.
How do these endocrine cells
differ ultrastructurally from typical cells responsible for exocrine
secretion?
Posterior
pituitary |