 Oral
Cavity -- contains structures for ingestion and fragmentation of
food, resulting in formation of a bolus of food for swallowing. Oral
Cavity -- contains structures for ingestion and fragmentation of
food, resulting in formation of a bolus of food for swallowing.
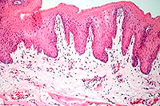
Examine a section of a lip (slide 67
and slide 134).
The skin on the external surface (with hair) merges into the nonkeratinized, stratified squamous epithelium
oral mucosa on the
internal surface (Fig. 15-3).
- Note the abundance of skeletal
muscle and small salivary glands in the lip.
Examine a section of an adult tooth
(slide 129), which is from a decalcified tooth still embedded in the
bone of the jaw. The enamel is completely dissolved away, since this
is almost completely calcified material, with little organic
content. The section is not well-stained, but resembles the diagram
in Fig. 15-7. Starting inside the tooth, identify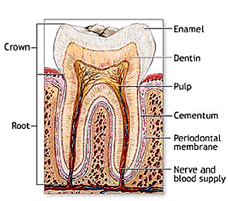
- Dental pulp (Fig. 15-12),
- Odontoblasts,
- Predentine, and
- Dentine (Figs. 15-12).
On the outer surface of the tooth,
identify
- Bone,
- Periodontal membrane or
ligament,
- Cementum, dentine, and
- The gingiva (Fig. 15-7b and
15-13).
What type of connective tissue is the
periodontal membrane? The dental pulp?
What does the presence of dentine in
this decalcified slide tell you about its composition?
What is the significance of the fine
parallel lines that can be seen in the predentine?
Does dentine continue to be made in
an erupted tooth?
Developing
tooth and the tongue. |