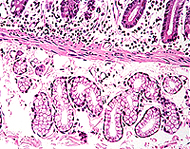
 Identify
Brunner's glands (Fig. 15-34) and small aggregates of lymphocytes on
slide 4. Classify Brunner’s glands as to staining property (serous
or mucous) and mode of secretion. Identify
Brunner's glands (Fig. 15-34) and small aggregates of lymphocytes on
slide 4. Classify Brunner’s glands as to staining property (serous
or mucous) and mode of secretion.
On slide 4 find groups of villi cut
longitudinally and identify
- Capillaries,
- Lacteals, and
- Smooth muscle
fibers in the lamina propria of each villus (Fig. 15-33).
Then
examine the epithelial surface of the villi, identifying goblet
cells, the striated border on enterocytes, and crypts at the bases
of adjacent villi (Fig. 15-27 and 15-28). Identify mitotic figures
in epithelial cells of the crypts. Paneth cells (Fig. 15-30) in the
lining of the crypts are best seen on slides
50 and
37, which are
H&E stained.
 Which is more readily visible
in a villus, the capillaries or the lacteal? Which is more readily visible
in a villus, the capillaries or the lacteal?
Why are enterocytes said to
have a “striated or brush border?”
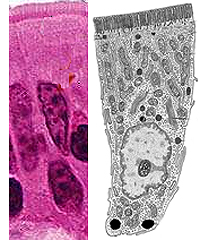
Examine the ultrastructural features
of enterocytes, especially their apical and basal surfaces,
in Fig. 15-28 and 15-29.
- Note at the apical end especially the
glycocalyx, microvilli,
- The terminal web, and
- The formation of endocytotic vesicles
At the
basal-lateral surface, note the close association with a capillary
for transfer of absorbed molecules and the movement of fatty chylomicrons from the
intercellular cleft into the lamina propria
for uptake by lacteals.
What is the functional
significance of each of the following?
- glycocalyx on microvilli:
- endocytotic vesicles:
- intercellular cleft:
But things
don't always go as designed. |