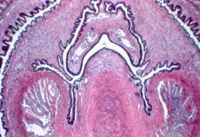
 Examine
a section of the penis (slide 109)
and identify the folded mucosa of the urethra (Fig. 21-18 and 21-19). What type of epithelium is present? Near
the urethra, identify the small paraurethral glands (Fig.
21-19). Examine
a section of the penis (slide 109)
and identify the folded mucosa of the urethra (Fig. 21-18 and 21-19). What type of epithelium is present? Near
the urethra, identify the small paraurethral glands (Fig.
21-19).What larger glands supplement
the paraurethral glands and what is the function of these glands?
Identify the corpus cavernosum
urethrae (or corpus spongiosum) surrounding the urethra (Figs.21-17
and 21-18). Next to this, dorsally, identify the paired corpora cavernosa penis. These
bodies together represent three cylinders of erectile
cavernous tissue. Within them identify the helicine arteries and the
large vascular sinuses in the connective tissue surrounding the arteries
(Fig. 21-19).
Would you classify the helicine
arteries as actual arteries or as arterioles?
How does the action of these
blood vessels lead to erection of the penis?
Clinical note: The target of
the drug Viagra, used to treat impotence or erectile dysfunction, is
the population of smooth muscle cells in the microvasculature of the
corpora cavernosa, increasing the contractility of these cells and
facilitating the events that lead to the cavernous tissue filling
with blood.
Now for the
female reproductive system. |