Now
look for elastic fibers in the tunica media (middle layer) of the
aorta wall (slide 100)
(Fig. 5-13).
- Their ultrastructural appearance
is found in Fig. 5-14.
- On slide
92 examine the internal
and external elastic laminae on either side of the tunica media
(Fig. 11-8).
What cell type(s) produces
elastic fibers and how is this type of CT functionally different
from "dense" CT?
Examine slides
92 and
45 for examples
of white adipose tissue (Fig. 6-1).
In the living condition, what
is contained in the wide empty spaces of this tissue?
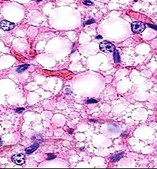 Compare the differences
between white and brown (photo to the right) adipose tissue (Figs.
6-1 and 6-4). Compare the differences
between white and brown (photo to the right) adipose tissue (Figs.
6-1 and 6-4).
What are the structural
differences between white and brown adipose tissue?
Where is brown adipose tissue
usually found in humans and why?
How do the structural features
of brown fat (and its differences from white adipose tissue)
facilitate its major function?
Next comes cartilage and bone. |