Examine a smear made from a bone
marrow aspirate (slide 127)
- Focusing on a region near the
end of the slide where the smear is relatively thin and cell
morphology is good.
- Note that most of the cells
present are mature red and white blood cells like those in the
smear of
 circulating blood. circulating blood.
- What could have caused the
empty circular areas that are seen?
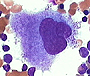
Identify megakaryocytes (Fig.
13-11)
and note their very large, polyploid nuclei.
Give three ways in which megakaryocytes differ from the other
types of leukocytes.
Look
for erythrocyte precursors (Fig. 13-5), including
- Proerythroblasts, and
- Normoblasts of different stages
(early, intermediate, and late)
- Reticulocytes can only be
distinguished from mature erythrocytes by using a special stain
for their RNA content (Fig. 13-5)..
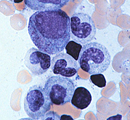 Look for granulocyte precursors (Fig.
13-8): Look for granulocyte precursors (Fig.
13-8):
- Myelocytes,
- Metamyelocytes, and
- Stab cells.
In a bone marrow transplant,
what cells are transplanted and what is the goal of the procedure?
Clinical note: Leukemias are
malignancies arising from the hemopoietic precursors of leukocytes
and are classified as lymphocytic leukemia or myelogenous leukemia,
depending on whether lymphocytes or granulocytes are involved.
Next is the
muscle unit. |