Schwann cells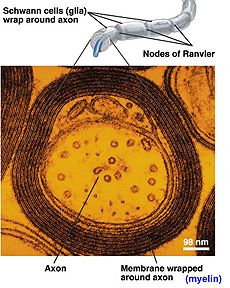
Examine the preparation of isolated,
teased-apart nerve fibers (slide 151).
- Identify Schwann cell nuclei and
nodes of Ranvier (Figs. 9-23 and 9-26).
- Study the diagrams and electron
micrographs in Figs. 9-21 through 9-25 and understand the relationship
between the axon and the myelin sheath wrappings in myelinated
nerve fibers.
- Click the image for an
expanded
view.
What exactly is "myelin"?
How are Schwann cells
associated with both myelinated and non-myelinated fibers of
peripheral nerves?
Synapses and Sensory Receptors
are very difficult to demonstrate in routinely prepared microscope
slides. We will study them primarily in electron micrographs and
other figures in Junqueira, although certain receptors will be seen in
slides later in the course.
Examine the electron micrographs and
diagrams of synapses
in the CNS (Figs. 9-6 and 9-7) and a motor end plate (or neuromuscular junction) (Fig.
10-13).
- Identify synaptic vesicles in
the axon's terminal bouton, synaptic vesicles, presynaptic
membrane, and postsynaptic membrane.
Draw all the parts of a typical
synapse, labeling the features listed above.
Tell me more about
sensory receptors. |