 Peripheral
Nerves usually contain axons from Peripheral
Nerves usually contain axons from
- Motor,
- Sensory, and
- Autonomic neurons
- All mixed in bundles organized
into fascicles by CT coverings.
Examine sections of small autonomic
ganglia and small peripheral nerves (Fig. 9-28) in loose CT (slide
45) and identify the Schwann (glial) cells.
What are some distinctive
features of small peripheral nerves in sections of loose CT?
What other tissue types do
small peripheral nerves cut longitudinally resemble slightly?
Examine the cross-section of a large
peripheral nerve (Fig. 9-26 and 9-27) in
slide 150.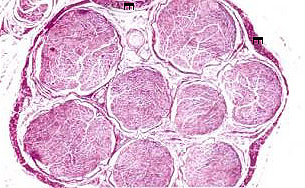
- This section has been prepared
with osmium to preserve lipids of myelin and stain this material
black. Identify
- epineurium,
- perineurium, and
- endoneurium.
- Identify
- myelinated and non-myelinated
fibers.
- Study electron micrographs of
myelinated and non-myelinated nerve fibers (Fig. 9-27)
and correlate these with the section on
slide 150.
The perineurium along with the nature
of the capillaries in the endoneurium make up a “blood-nerve
barrier” that helps protect the myelin sheathes of peripheral nerves
from viral or immunological agents.
Ever wonder about
Schwann cells? |