Microscopic features of the eye: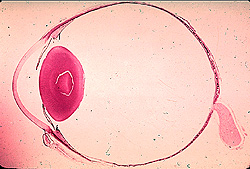
- Review the general organization of
the eye (Fig. 23-1).
- Examine a section of the eye
(slides 78 and 120) with low power and, from anterior to
posterior, identify
- The cornea,
- Iris,
- Lens,
- Ciliary body,
- Retina, and
- Optic nerve (Fig. 23-1).
List the structures of the eye
that contain dark melanin pigment.
In what ocular structure is most
muscle found and what type of muscle is it?
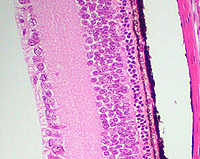 With
higher power, examine the retina carefully and note capillaries and
the ten layers shown on Fig. 23-15. With
higher power, examine the retina carefully and note capillaries and
the ten layers shown on Fig. 23-15.
- Within these layers, identify the
pigmented epithelial cells, the rods and cones (Fig. 23-16),
- The 3 layers of cell bodies, the
inner and outer plexiform layers, and the inner limiting membrane
(Fig. 23-15).
- Determine whether the fovea (Fig.
23-14) or the optic disc (where the optic nerve meets incoming axons
from the retina, Fig. 23-14), is present on your slide and if not
share your neighbor's slide to observe these structures.
How do the cells in the retinal
layers interact to send visual information to the brain?
What is the significance of the
structural differences seen at the fovea centralis?
What is the optic disk and what is
its functional significance?
More about the
eye. |