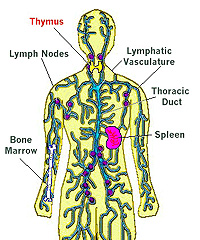
 Lymphoid
tissue and organs, along with the lymphatic vessels constitute a
very widespread and extremely important immune defense system and a
filtering system between the body tissues (where foreign substances
and organisms can gain entrance) and the blood stream. The structure
of lymphatic vessels was considered with the circulatory system in a
previous exercise. Lymphoid
tissue and organs, along with the lymphatic vessels constitute a
very widespread and extremely important immune defense system and a
filtering system between the body tissues (where foreign substances
and organisms can gain entrance) and the blood stream. The structure
of lymphatic vessels was considered with the circulatory system in a
previous exercise.This
laboratory exercise will deal primarily with lymphoid tissue, which
consists of distinct lymphoid organs (the lymph nodes, thymus, and
spleen) as well as more diffuse collections of lymphocytes
(nodules), which are primarily located along the mucosa of the
digestive and respiratory tracts.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand that lymphoid organs
show a network of reticular fibers or epithelial tissue filled
with lymphocytes and other cells of the immune system.
- Distinguish and recognize the
specific unique structural features and regions of lymph nodes,
spleen, and thymus and understand the functional significance of
these features in each.
- Understand the circulation through
the lymph nodes and spleen and how these organs filter lymph and
blood respectively.
- Recognize the major unencapsulated
collections of lymphocytes in the mucosa-associated lymphoid
tissue (MALT), including tonsils, Peyer’s patches, and appendix.
The actors. |