 Cytoplasmic
Organization and Organelles Cytoplasmic
Organization and Organelles
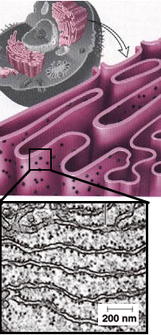
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (rER)
consists of a network of rounded or flattened membranous sacs (cisternae)
with polyribosomes covering much of the outer surface of the
cisternae (Fig. 2-15). Polypeptides synthesized on these ribosomes are deposited
inside the sacs for eventual delivery outside the plasma membrane.
Examine the different appearances of rER in Figures 2-14 through
2-17.
Since the RNA associated with rER is
basophilic, cytoplasm rich in rER shows basophilia with routine LM
stains, such as H&E. This is prominent in neurons, where the
basophilic patches in the cytoplasm are called Nissl or
chromatophilic substance (Fig. 9-3 and slide 71). Basophilic rER is also prominent in secretory
cells, where it is sometimes called ergastoplasm. An example of this
occurs near the nucleus of cells in the pancreas (Figs. 2-23 and
16-9 and slide 154).
What is the difference between
the functions of free polyribosomes and polyribosomes on rER?
Why is Nissl substance more
prominent in actively growing neurons?
Smooth
endoplasmic reticulum. |