Plasma Membrane of a cell
consists of a bilayer of phospholipids with many different
associated integral and peripheral proteins and glycoproteins (Fig. 2-2).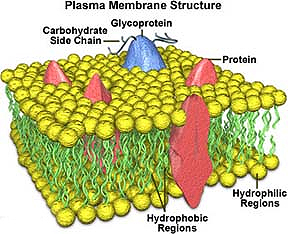
The cell’s plasma membrane, or
plasmalemma, is only 7 – 10 nm thick, below the resolution of the
light microscope.
- In very high magnification TEM
pictures, such as Fig. 2-1a, the structure of the plasma membrane can be partially
seen if the proteins associated with it internally and
externally are abundant.
- A thick external coat of
glycoproteins on the outside of the plasma membrane is called a
glycocalyx.
How does the well-known diagram
of the “fluid mosaic” membrane model shown in Fig. 2-2a correlate with the apparently
three-layered membrane structure shown in the EM of Fig. 2-1a?
How would expect a cell’s glycocalyx to stain with alcian
blue?
With the PAS reaction?
Let's now take a look at
membrane
bound organelles within the cell. |