|
Introduction
Case1:
Vomiting
Case 2:
Cough & fever
Case 3: Bruising
Case 4: Sore
throat
Case 5: Jaundice
Case 6: Flu & fever
Case 7: Diarrhea
Case 8: Black
Robe
Case 9: Back Pain Catching the
beast
Thanks to
Quiz
Please |
|
Mechanisms of microbial injury.
- They can kill the
host cell directly.
- Proliferate within the
cell, eventually causing cell rupture.
- Elaborate and release
enzymes locally that cause cell death.
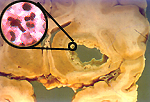
- An example: Staph
brain abscess
|
|
- Toxins.
- Exotoxins:
Cellular metabolites released into the environment.
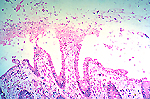
- C. difficile
enteritis (picture right)
- B. anthracis
- Endotoxins:
Cell wall fragments.
|
|
- Hypersensitivity
(the hosts immune system goes wild, destroying host tissue).
- Type I: IgE mediated (anaphylaxis)
- Type II: antibodies
cross react with host.
- Type III: antigen-antibody
complexes.
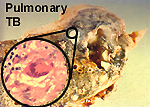
- Type IV: cell mediated
(tuberculosis)
|
|
Now you're scaring me.
What about host defenses
?
Back
|


