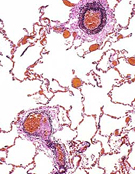
 Examine
slide 98, in which the lung section is stained to demonstrate
elastic fibers in the lamina propria of bronchioles and in the
tunica media of the larger arteries (Fig. 17-9b). Examine
slide 98, in which the lung section is stained to demonstrate
elastic fibers in the lamina propria of bronchioles and in the
tunica media of the larger arteries (Fig. 17-9b).
- In the visceral pleura note the
abundant elastic fibers mixed with collagen fibers.
- Finally note the dark elastic
fibers in the walls of alveoli.
What is the function of the
visceral pleura?
Would you say lung tissue
consists mostly of stroma or parenchyma?
On slide
97 or
98 use the low power
objective to locate a region showing the terminal portion of a
respiratory tree cut longitudinally as shown in Figs. 17-11 and
17-12. Identify
the terminal bronchiole, respiratory bronchiole, alveolar duct,
alveolar sac, and alveoli.
What differences in the
epithelium distinguish the first 3 components just listed?
At what point do the
capillaries in the airway wall become most important?
 Clinical note: Emphysema,
which is almost always due to the toxic effects of cigarette
smoking, produces alveolar loss and enlargement of the air spaces
beyond the terminal bronchioles due to chronic inflammation and the
gradual destruction of pneumocytes and interalveolar septa. This
reduces the total respiratory surface available for gas exchange,
producing inefficient respiration. The affected tissue does not
regenerate and the treatment includes the permanent use of
oxygen-enriched air. Clinical note: Emphysema,
which is almost always due to the toxic effects of cigarette
smoking, produces alveolar loss and enlargement of the air spaces
beyond the terminal bronchioles due to chronic inflammation and the
gradual destruction of pneumocytes and interalveolar septa. This
reduces the total respiratory surface available for gas exchange,
producing inefficient respiration. The affected tissue does not
regenerate and the treatment includes the permanent use of
oxygen-enriched air.
Pneumocytes and
macrophages. |