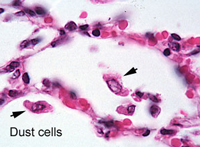
 Using
the 40X objective, carefully examine walls of alveoli (Fig. 17-14). Using
the 40X objective, carefully examine walls of alveoli (Fig. 17-14).
- Identify macrophages (dust
cells),
- The flattened type I pneumocytes,
and
- The rounded type II pneumocytes
(Fig. 17-14).
- Not many nuclei of type I cells
will be visible. Why?
Study the electron micrographs of the
alveolar wall (Fig. 17-15), the air-blood barrier, across which gas
exchange occurs (Fig. 17-13), and the surfactant-producing type II pneumocytes (Fig. 17-16). Also identify and note the location of
capillaries around every alveolus.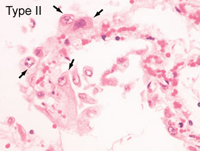
Specifically, across which
cells does gas exchange occur in the lungs and what is the
physiological role of the other cells in alveoli?
Make a sketch at high
magnification of an alveolus showing the components of the wall
separating air and blood.
Where might “dust cells”
(alveolar macrophages) be most common?
Now comes the
urinary system. |