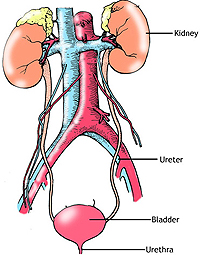
 The
urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra
and is responsible for the important bodily function of soluble
waste production, storage and elimination. The
urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra
and is responsible for the important bodily function of soluble
waste production, storage and elimination.
The waste substances are produced in the
kidney as blood filtrates, transported via the ureters to the
bladder where it is stored and eventually eliminated through the
urethra. This process also results in the salvaging of large amounts
of water, sugars and ions from the blood filtrate which are returned
to the blood. In addition, the kidneys play a role in controlling
systemic blood pressure by the secretion of renin.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the organization of
the kidney into lobes and lobules and their relationship to
cortical and medullary areas.
- Understand the arterial input
and venous drainage through the kidney’s micro vasculature.
- Understand the structure of the
renal corpuscle, including podocytes, and the ultrastructure of
the glomerular filter.
- Understand the locations of the
various parts of the nephron with respect to cortex and medulla.
- Identify all parts of the
nephron and collecting ducts in histological sections and
understand how the structures of the different regions
correspond to their functions.
- Recognize the structure and know
the function of the juxtaglomerular apparatus.
- Identify the key structural
features of the ureter, bladder, and urethra.
The basic
structure of the kidney. |