 Thyroid
gland -- secretes a hormone regulating the basal metabolic rate
and a hormone regulating blood calcium levels. Thyroid
gland -- secretes a hormone regulating the basal metabolic rate
and a hormone regulating blood calcium levels.
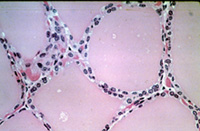
Examine a section of thyroid gland
attached to trachea on slide 2. Identify
thyroid follicles, composed
of follicle cells in a simple cuboidal epithelium, which are
organized into lobes by supporting tissue septa continuous with the
thin capsule (Fig. 20-19). Examine the electron micrograph of a
small thyroid follicle in Fig. 20-20.
Explain how thyroid follicle
cells produce thyroglobulin, store it, convert it to
iodine-containing thyroid hormones for secretion.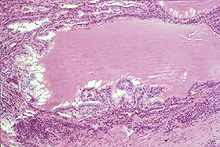
Clinical note: Increased
height of thyroid follicular cells and infoldings of the follicle
wall are indications of hyperthyroidism or Grave’s disease, a
disorder characterized by restlessness, sleeplessness, tremor, and a
noticeable exophthalmos. Treatment is by subtotal thyroidectomy or
use of radioactive iodine to destroy or inactivate thyroid
follicles.
Identify the calcitonin-secreting,
pale parafollicular cells (or clear cells; Figs. 20-19 and
20-20), which are
closely associated with the thyroid follicles but are not usually in
contact with their lumens. With the light microscope, parafollicular
cells can be very difficult to distinguish from follicle cells.
How do the origins of these two
cell types differ embryologically?
Why do you think parafollicular
cells stain much less heavily than follicular cells?
Parathyroids
are next. |