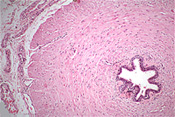
 Examine
the vas (or ductus) deferens (slide 152) with its three
prominent layers of smooth muscle (Fig. 21-12) for rapid,
peristaltic expulsion of sperm from the epididymis. Examine
the vas (or ductus) deferens (slide 152) with its three
prominent layers of smooth muscle (Fig. 21-12) for rapid,
peristaltic expulsion of sperm from the epididymis.
Where are the smooth muscle layers more
prominent, in the vas deferens or the epididymis, and why?
Examine a transverse section of the
spermatic cord (slide 52), which besides the
vas deferens contains
arteries, veins, nerves, etc. embedded in loose support tissue.
When a portion of this duct is
removed in a vasectomy, what happens to the sperm in the epididymis?
Glands -- paired seminal vesicles
and the prostate gland, both with highly folded secretory mucosae
within distinct capsules. The anatomical relationship these glands
to the urinary bladder is shown on the next page.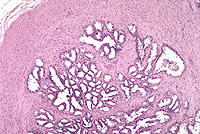
Examine a section of the seminal
vesicle (slide 124). Identify columnar/cuboidal epithelium (it may
appear pseudostratified) on the thin, highly folded lamina propria
and the very prominent wall of smooth muscle surrounding the
secretory components (Figs. 21-13 and 21-14).
What do the seminal vesicles
secrete?
Now for the prostate. |