 Ectocervix,
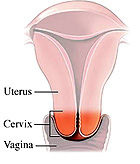
Cervix and Vagina -- The cervix is the narrow portion of the
uterus protruding down in to the upper vagina. Ectocervix,
Cervix and Vagina -- The cervix is the narrow portion of the
uterus protruding down in to the upper vagina.
Slide 133 has a transversely-sectioned
specimen of the uterine cervix showing the epithelium of the cervix
or ectocervix. The plane of the section is as shown in the diagram
below.
At one end of the section, locate the
narrow slit lined mainly by simple columnar cells. This space is an
endocervical gland. The opposite end of the section is
covered by the stratified squamous epithelium of the ectocervix,
similar to that of the vagina (Fig. 22-22). Note that most of the
tissue in the uterine cervix is fibrous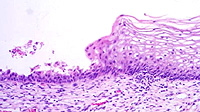 (myometrial)
tissue with a relatively small amount of smooth muscle but many
vascular sinuses. (myometrial)
tissue with a relatively small amount of smooth muscle but many
vascular sinuses.
Which cells or tissue on
slide
133 are examined in a Pap test and how are they obtained?
Clinical note: The Pap test is
named after the New York gynecologist George Papanicolaou, M.D., who
introduced this diagnostic procedure in 1928.
The breast is next. |