Cell Biology & Histology A560
There are two types of bone
development: intramembranous and endochondral ossification or
osteogenesis.
-
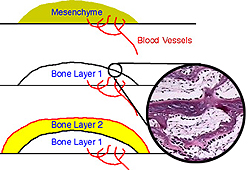 Intramembranous
ossification gives rise to membrane bones, these being the
flat bones of the skull and parts of the mandible. Intramembranous
ossification gives rise to membrane bones, these being the
flat bones of the skull and parts of the mandible.
- This process involves the
deposition of bone matrix (osteoid) directly in regions
("membranes") of embryonic mesenchyme.
-
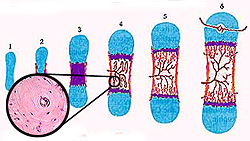 Bones of the extremities,
pelvis and vertebral column (cartilage bones) are formed by
endochondral ossification. Bones of the extremities,
pelvis and vertebral column (cartilage bones) are formed by
endochondral ossification.
- This process involves the
replacement of a hyaline cartilage model with bone.
Regardless of the ossification process, the histological
structure of the bone is the same.
Learning Objectives:
- Understand the differences and
similarities between intramembranous and endochondral bone
formation and the key function of the periosteum in bone growth.
- Understand the organization of
the epiphyseal growth plate and its role in endochondral bone
formation and growth of long bones.
- Understand the structure of a
typical synovial joint, including the nature and functions of
the synovium.
Let's look at
some examples. |
|