Examine glial cells and other types
of neurons in a section of the cerebellum (slide
71 or
148). Using
Fig. 9-6 as a guide, look for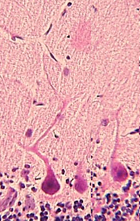
- Neurons of the molecular layer,
- The granular layer, and
- The very large Purkinje cells (a
type of neuron) at the boundary between these layers.
Also on
slide 71, examine the
distinctive choroid plexus (Fig. 9-20), with epithelial cells
covering a mass of capillaries and pia mater.
What is the function of the
choroid plexus?
Examine a section of spinal cord
(slides 9,
149). The tissue is somewhatcrd1.jpg) disrupted, but identify the central gray matter, containing motor
neurons, “interneurons”,
the central canal lined by ependymal
cells (Fig. 9-12), and the outer white matter, consisting largely of
myelinated fiber tracts (Fig. 9-14).
disrupted, but identify the central gray matter, containing motor
neurons, “interneurons”,
the central canal lined by ependymal
cells (Fig. 9-12), and the outer white matter, consisting largely of
myelinated fiber tracts (Fig. 9-14).
Where are most of the neurons and
what is the major glial cell of white matter?
Clinical note: The CNS is
subject to various diseases in which there is destruction of the
myelin sheaths, such as multiple sclerosis (MS). The functions and
body regions affected by MS depend on where in the CNS the focal
areas of demyelination occur. Weakness and paralysis of one or more
limbs are common sequelae of this disease.
Now for ganglia. |