|
Introduction
Case1:
Vomiting
Case 2:
Cough & fever
Case 3: Bruising
Case 4: Sore
throat
Case 5: Jaundice
Case 6: Flu & fever
Case 7: Diarrhea
Case 8: Black
Robe
Case 9: Back Pain Catching the
beast
Thanks to
Quiz
Please |
|
Clostridium
species important in human infections:
Anaerobic, gram +, spore forming rod.
- C. perfringens: wounds or
contaminated surgery; cellulitis,
myonecrosis, septic abortions.
- C. tetani: wounds, neonatal
umbilical stump, toxin causes tetany.
- C. botulinum: neurotoxin
from contaminated food or GI colonization.
- C. difficile: overgrows GI
flora, toxins cause pseudomembranous colitis.
|
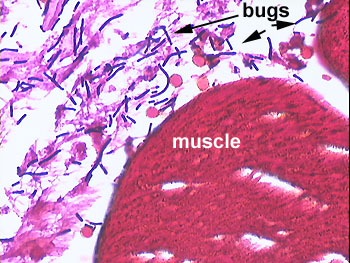 |
- All clostridial species secrete toxins and
tissue destroying enzymes.
- Clostridium perfringens makes at least
twelve. Here are just a few:
- Collagenase and hyaluronidase that degrade
extracellular matrix.
- Alpha toxin degrades lecithin, destroying
membranes.
- Theta toxin, binds to cholesterol causing
membrane destruction.
- Results in WBC lysis. Note in the picture
above there are no polys.
- Therapy for C. perfringens
infection consists of:
- Wide debridement of necrotic
tissue.
- Antibiotic therapy (penicillin), but it
can be tough to get high tissue levels in devascularized, necrotic
tissue.
- Possibly even hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
|
|
So how do we capture and
identify the culprit?
Back
|
