|
|
|
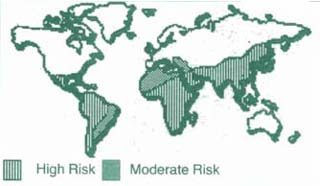
Typhoid fever
- Largely a disease of developing
countries.
- Caused by Salmonella typhi
- Humans are only host.
- Shed in urine, feces, vomitus and oral
secretions.
- Spread by poor sanitary conditions.
|
 |
- Invasion of intestinal epithelium,
triggered by low oxygen tension of gut.
- Bacteremia, fever, chills during the
first week.
- Culture blood or bone marrow.
- Widespread reticuloendothelial
invlovment, abdominal pain and prostration in the second week.
- Organisms grow inside the macrophages.
- Ulceration of Peyer's patches,
intestinal bleeding and shock may follow.
- Even though high fevers, patient may
exhibit:
- Bradycardia and
- Leukopenia
- Marked splenomegaly and hepatomegaly.
- Treat with chloramphenicol,
- If resistant, Cipro or third generation
cephalosporin.
|
Now comes a man with fever
and nausea.
|
