|
|
|
Nutrition and Diagnosis-Related
Care
|
|
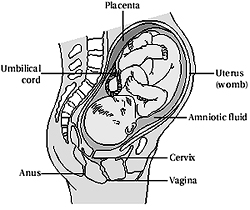 Pregnancy is an anabolic state as attested
to by the expected growth of maternal tissues, to say nothing of the
fetus and placenta. Pregnancy is an anabolic state as attested
to by the expected growth of maternal tissues, to say nothing of the
fetus and placenta.
- The net caloric cost of carrying a
singleton pregnancy is 80,000 kcal.
- Amino acid, vitamin and mineral needs
are also substantially increased.
What are the basic nutritional
objectives?
- Meet the increased needs of maternal
and fetal tissues, but at the same time prevent hyperglycemia and
hypoglycemia and associated ketosis.
- Provide adequate amino acids and
minerals.
- Approximately 1 kg of protein
will be made by the fetus and placenta.
- Adequate iodine is critical for
both maternal fetal thyroid function.
-
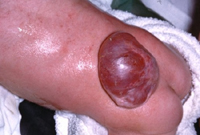 Increase
vitamin intake, especially folic acid. Increase
vitamin intake, especially folic acid.
- Folic acid and iron deficiency
occurs in 50-75% of pregnancies.
- Folic acid deficiency and
neural tube defects, click image.
- Vitamin D deficiency is
associated with low infant birth weight.
- Encourage proper rate of weight gain
during pregnancy. For the average woman.
- 1st trimester, 2-4 pounds
- 2nd trimester, 10-11 pounds
- 3rd trimester, 12-13 pounds
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco, moderate
caffeine intake only.
- Be cautious of excess salt intake
and maternal hypertension.
Mrs. Franklin's history of
bulimia greatly complicates
things. |
|